Latest
Update
Today's Top Highlights
Explore the intersection of technology and creativity through storytelling in the digital era.



President Trump Alleges New York Times of Being Democrats Mouthpiece in Defamation Case
By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025

Sportswoman Braces to Face Life Without All Limbs Following Devastating Sepsis Struggle
By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025


A Look at Diplo: The Mighty Dinosaur – Kids’ Dinosaur Animation Turns Self-Aware Rebelling On ‘Cute’
By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025

The Mighty Dinosaur Diplo Critique – Children’s Dino Animated Film Breaks the Fourth Wall Revolting Versus ‘Sweet’
By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025

The US President's Official Trip to the UK: Key Agenda Points
By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025

Political Abuse: Brazil Official Denounces US Revoking Their Young Child's Visa
By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025

Diplomatic Abuse: Brazil Official Condemns US Revoking His 10-Year-Old Child's Visa
By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025

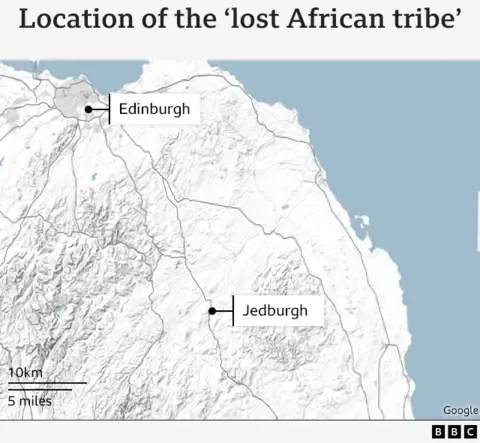
Clearance of So-Called ‘Tribe’ from Scottish Woodland Site Starts
By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025
September 2025 Blog Roll
August 2025 Blog Roll
July 2025 Blog Roll
June 2025 Blog Roll
Popular Posts
Sponsored News
 News
News
Bengals Persist Operating As If They’re In A Fantasy League, and Burrow Keeps Bearing the Heavy Cost
 By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025
By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025
 News
News
Belgian-Moroccan Artist Declares: ‘Creatives Can Be Storytellers That Invent Narratives – However They Uncover Much’
 By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025
By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025
 News
News
 News
News
Keir Starmer Presides Over Cabinet Meeting As Rising Tensions After Departure of Key Staffer
 By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025
By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025
 News
News
Clutch Mayfield Magic Secures Exciting Victory Over Texans
 By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025
By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025
 News
News
India and United States Engage in Full-Day Trade Negotiations
 By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025
By Jennifer Moyer
•
16 Sep 2025




